Article Excerpt
3D printing can produce a house in only a few days. How do 3D-printed houses compare to other homes? Read on to learn more.
3D printing, more formally known as additive manufacturing, has gone from a mysterious sci-fi concept to a common process in a remarkably short period of time. Some companies have been experimenting with using 3D-printing technology in construction.
An Austin-based company has created multiple 3D-printed homes and plans to build more. The technology offers the possibility of significantly faster construction at lower costs. It also has several drawbacks, partly based on the fact that 3D printing is still a new technology with more than a few glitches. Most homebuyers probably won’t have access to 3D-printed homes for a while, but it is worth looking at the technology and what it could offer.
What Are 3D-Printed Homes?
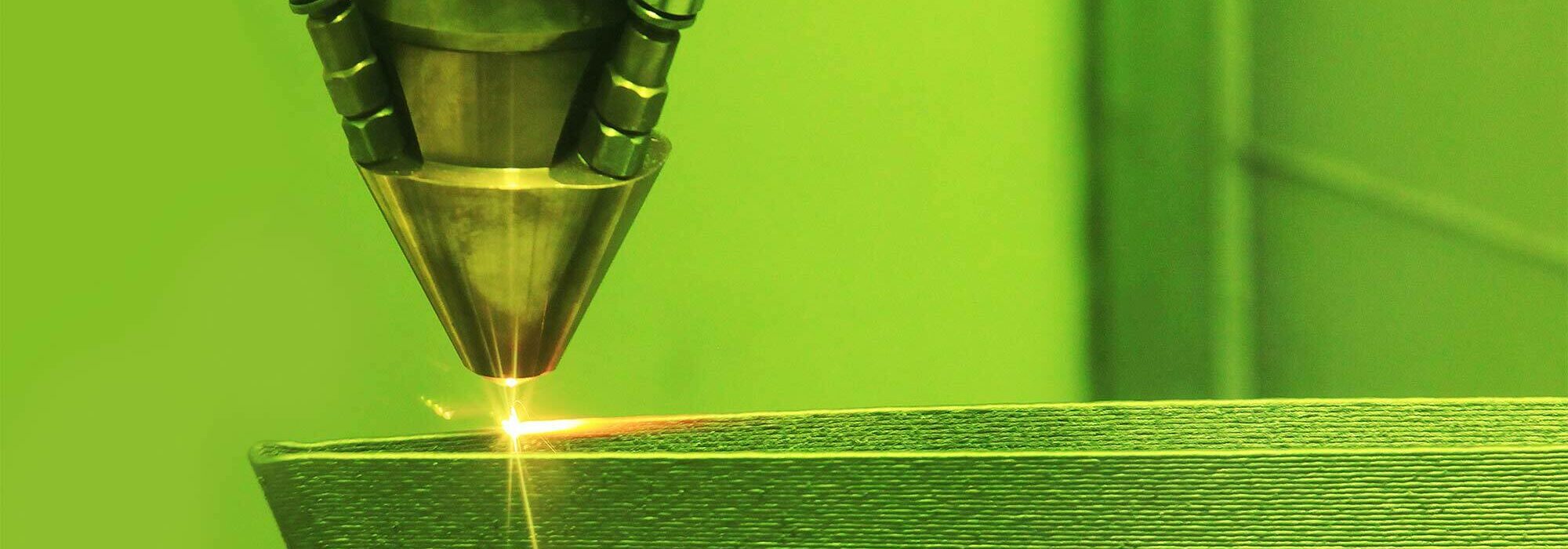
All 3D printers, regardless of size, use the same basic process to create three-dimensional objects. They use a nozzle to deposit layers of materials according to a 3D computer model. The technology first caught on in the 1980s as a way to produce prototype models quickly. It has grown to include a wide range of manufacturing parts, medical equipment, prosthetic devices, and even food.
Similar to how inkjet printers can print combinations of colors on paper, many 3D printers can combine various materials to create objects. The devices used to create 3D-printed homes use concrete to produce walls one layer at a time.

How Are 3D-Printed Homes Built?
Two methods are possible for 3D-printed homes. They can use prefabricated walls produced off-site, or they can be created on-site using a very large 3D printer. This device consists of a large nozzle on a gantry or a robotic arm that allows it to move around the construction area. 3D-printed homes currently only use concrete in the printing process. Builders are experimenting with other materials, such as clay and plastic.
Builders typically begin with a poured foundation. The 3D printer then creates the walls by depositing layers of concrete based on a 3D computer design. It can create solid concrete walls, or they can be hollow to allow for insulation. It can also create columns to provide additional structural support. 3D-printed roofs are still in the experimental stage, so most current 3D-printed houses have roofs built the old-fashioned way.
How Much Do 3D-Printed Homes Cost?
The cost of building a 3D-printed home is supposedly much lower than a traditional home, or even a tiny house. An Austin company has stated that it can create a 350-square-foot 3D-printed home for $4,000, with a possible retail price of $10,000.
» READ MORE: Mortgage Financing for Tiny Homes
With new-home costs in the $400,000-$500,000 range, this seems like quite a bargain. Keep in mind, however, that very few companies are currently capable of producing 3D-printed homes. The equipment needed to 3D-print a house can cost anywhere from $180,000 to over $1 million. It remains to be seen whether 3D-printed homes will become a common or sought-after style.
One Austin-based company is in the process of building 100 3- and 4-bedroom 3D-printed homes in Georgetown, just north of Austin, in partnership with a major homebuilder. News reports suggest that the cost savings are not as much as we might have hoped. The finished homes will go on the market next year for around $400,000. The company has said that it hopes it will be able to scale its operations, and that this will bring costs down.
![Photo by Misanthropic One on Wikimedia Commons [Creative Commons] 3D-printer making concrete shapes.](/images/articles/_generalPhotoStandard/3_2022-12-21-183516_uzsm.jpg)
Photo by Misanthropic One on Wikimedia Commons [Creative Commons]
How do 3D-Printed Homes Compare to Homes Built With Traditional Construction?
A 3D-printed home offers some potential advantages over a home that uses traditional construction techniques. Many of these advantages remain largely theoretical, given how new the technology is. 3D printing also presents some disadvantages.
Pros of 3D-Printed Homes
Lower Costs
The basic cost of 3D-printing a house is considerably less than the cost of building a traditional house. The construction process requires less labor and storage of materials. Other factors may offset this benefit, but for now, it is too early to say for certain what that effect will be.
Versatility of Design
3D printing is giving designers and architects new opportunities to try forms that would not work with other building materials. Many 3D-printed homes are using curved walls, for example, in ways that might not have been possible before. Builders will save design files on computers which can they be replicated for another house. They'll team up with experts to understand cutting-edge industrial design essentials and advantages and also to register their 3D designs as intellectual property. Pretty cool stuff.
Faster Construction
Building a house can take months. The main 3D-printing process can take as little as 48 hours to produce the main parts of a house.
Less Waste
A construction site using a 3D printer is likely to produce far less waste since nearly all of the materials go into the house. Additionally, the cement used in 3D printing often incorporates recycled materials, which further cuts down on waste.
Durability
Concrete is a highly durable material. While the oldest 3D-printed buildings in the world are still quite young, they are likely to be able to withstand all sorts of weather conditions.
![Photo by Scott Lewis on Flickr [Creative Commons] Render of a partially finished 3D-printed home.](/images/articles/_generalPhotoStandard/4_2022-12-21-183722_atnq.jpg)
Photo by Scott Lewis on Flickr [Creative Commons]
Cons of 3D-Printed Homes
Developing Technology
Like any new technology, 3D printing still has many bugs to work out. Very few companies work with 3D-printed homes right now. Few home professionals, such as electricians, plumbers, and roofers, have experience with the issues the 3D-printed homes may present.
Visible Layer Lines
The 3D-printing process unavoidably leaves layer lines in the concrete. This creates a distinctive look, but if you want any other kind of look, including any sort of flat or paintable surface, you will need to add material like plaster.
Material Shortages
The 3D-printing process for houses requires specific composite materials that are strong enough for use in construction. These materials can be difficult to obtain at times, leading to the ongoing possibility of shortages.
Limited Size (For Now)
Most 3D printers that are currently available for home construction can only build homes with fairly small footprints. 3D-printed homes are also limited to one story right now. This may change as technology advances.
Workforce Disruption
It bears mentioning that if 3D-printed homes take off in popularity, it could have a major impact on the contracting professions.
Get Started With a Mortgage Lender You Can Trust
If you plan to use a mortgage to buy your next home, getting pre-approved for one is your first step. We’ll review what kinds of properties are eligible for purchase along with the best mortgage option for you. Getting started is easy. Answer a few questions and we’ll reach out to you!



